By
CHEKWI BENWIE
MEDICINE 1
SCIENTIFIC JOURNAL
CLUB
Faculty of Health Sciences
University of Bamenda, Cameroon
TANLAKA LUCAS MENGNJO
MEDICINE 2
SCIENTIFIC JOURNAL
CLUB
Faculty of Health Sciences
University of Bamenda, Cameroon
tanlakalucas@gmail.com
TRYING TO LOOSE WEIGHT BY DIET ALTERATION
Human beings are
often posed with several tragedies among which we have the assertion that it is
easier to gain weight than to lose it. In order to detect the cause of this
reality, we will take a closer look at the TCA cycle, particularly, the
decarboxylation reactions.
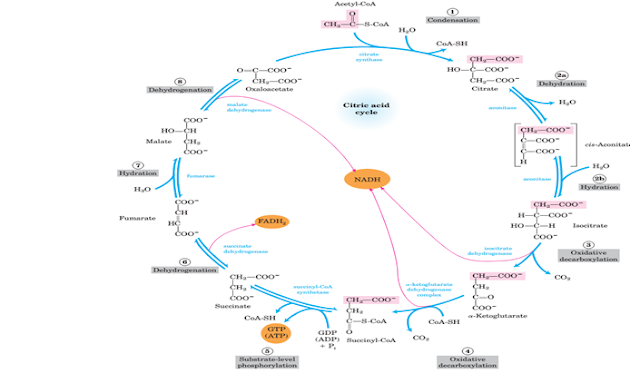
The surplus of
the food (carbohydrates, proteins and lipids) we consume can be stored as
triacylglycerols in adipose tissue. Also these biomolecules are
interconvertible except fats which cannot be converted to
carbohydrates. Fats gain their way into
the citric acid cycle through the formation of acetyl CoA fed into the
TCA pathway by β oxidation of fatty acids. For this to happen, acetyl CoA fed into the TCA pathway will have to yield oxaloacetate, the main precursor for gluconeogenesis. However, the two carbon atoms influxed
into this pathway are lost in 2 decarboxylation reactions to produce CO2.
Regardless of which compound owned the two carbon atoms, a two carbon loss is a
two carbon loss. This results in the disparity in anabolic and catabolic
pathway as in the diagram below.
As we have
already seen above, fats cannot yield carbohydrates. Glycemia (blood sugar
level) is a very critical physiological condition which needs to be regulated.
This is because the brain uses gluocose
as its main metabolic fuel. To a lesser extent, like in the case of extreme starvation,
the brain can switch to using acetoacetate (ketone body) as a fuel. This can be problematic because ketone bodies are fats and are obviously derived from a
nearby source; the meningeal covering of the brain. Therefore, much of our
metabolism is tilted towards protecting the master of the body (brain).
The surplus food
we consume is stored as fats. If we choose to limit our calorie intake (place
ourselves on a diet), the fat stores are mobilized to produce energy. This can lead weight loss. To maintain the normal glycemic level, our bodies release
glucagon and adrenaline to breakdown glycogen to produce glucose (glycogenolysis in liver).
Unfortunately,
we eventually become hypoglycemic. this is because our glycogen reserves run out since there
is little or no intake of carbohydrates. Prior to prolonged hypoglycemia, Growth Hormone and Cortisol are also released. They both decrease glucose
utilization by most cells including brain cells. Consequently we become
depressed, sluggish and easily irritated. We then start conceiving negative
thoughts like "this diet issue is completely pointless, a piece
of chocolate cake won't kill me". If we consider our diet, our body now switches
to using proteins to maintain blood glucose level. Proteins are converted to
pyruvate after being degraded to amino acids .
Hence, we lose muscle as we lose fat.
LOOSING
WEIGHT BY EXERCISE
Nonetheless,
there is a better and easier way of losing weight, that is, excersise . Appropriate
excersice can train our body to use all the fat stores in adipose tissues to
supply the tricarboxylic cycle with acetyl CoA through beta oxidation. If we maintain our normal blood glucose level, we save our
proteins and we have enough carbohydrates to maintain our glycogen stores. With a balanced ratio of exercise to food
intake (balance intake of nutrients), our fat degradation can be increased
without sacrificing our carbohydrate or proteins.Sample applications are
illustrated by the following
figure
|
The figure above shows a woman in the initial state with
extended and/or deformed abdomen (image on the left ). The image
on the right shows this same woman
who regained normal size, weight and
form by simply constantly doing exercise without necessarily restricting her diet.
Adopt the "training-off weight" method
of life ,regain and
conserve your normal weight and form.
|
References
BIOCHEMISTRY International
student edition 6th edition
Campbell /FARRELL . chap 19
biochemical connections page 572
GUYTON AND HALL textbook of
medical physiology . 12th edition chapter 78 unit XIV
DAVID L. NELSON and MICHAIL M. COX, Lehninga PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY,Fourth
Edition,Chapters: 15,16.Pages:536,607 ,Figure:14-10,16-7
Bossip.com/945926/weight-loss-sorcery
a gallery of shockingbefore and after
waist training photos


I think training off one's weight can really help people lose weight then restricting one's self from food.
ReplyDeleteHowever, practicing healthy diet can prevent weight gain.